The Shared Responsibility Model – an Important Basis of Cloud Security
Sebastian Grau from root360 provides an overview of the security responsibilities for companies, MSPs and cloud service providers for safeguarding sensitive data.

© Leyn| istockphoto.com
The shared responsibility model is an important basis for any cloud security concept. In case of lack of care, security issues can quickly arise. The shared responsibility model was therefore specifically developed by public cloud providers to clarify responsibilities in this area. But what exactly is behind it?
What is the shared responsibility model?
The shared responsibility model stands for shared responsibility in the two areas: “security of the cloud” and “security in the cloud”.
To give you an example: As a cloud provider, AWS is responsible for protecting the physical infrastructure and therefore for the security of the cloud. As an AWS customer, you either take care of security in the cloud yourself or you outsource it to a managed service provider, such as root360. This affects companies that use AWS in the infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) model.
The shared responsibility in detail
The following diagram illustrates the Shared Responsibility Model:
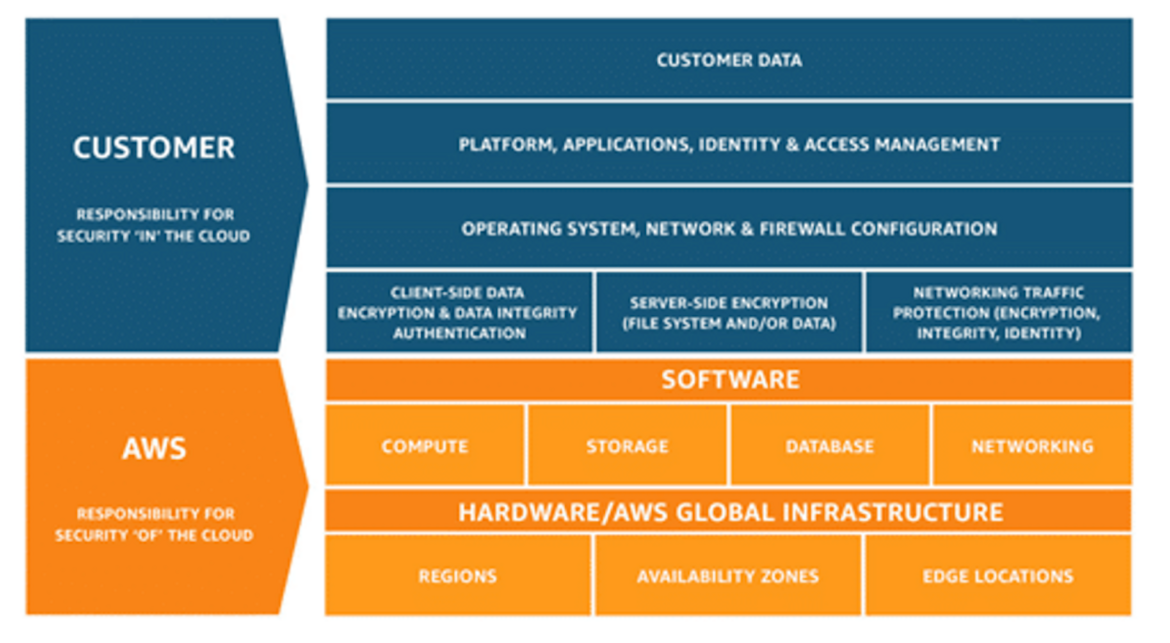
As you can see in the diagram, in this scenario, AWS as a public cloud provider is responsible for the security of the global infrastructure, meaning the data center infrastructure that runs all AWS services. So, AWS is responsible for the physical security of these data centers. Security measures in this area include, for example, continuous training and safety-related awareness of employees, the implementation of protective measures against environmental and weather damage, and constant monitoring of the data center.
The public cloud provider is also responsible for the security of the basic resources, which are grouped into the areas of compute, storage, database, and networking. Coming back to the scenario above, AWS is therefore responsible for ensuring the availability of physical hardware and the underlying infrastructure that enables customers to use AWS services securely. Third-party auditors regularly test and review the effectiveness of the security measures as part of AWS compliance programs.
Now let's look at the areas that the customers of public cloud providers are responsible for:
- Customer data — customers are responsible for securing the data they import or store into the cloud infrastructure. This means that you also must think about a security concept for “data-at-rest and -in-transit”. AWS offers various services in this area, such as AWS Key Management Service (KMS).
- Application — Every application that is used within the cloud infrastructure must be securely configured by customers. Security patches for the application also must be applied by the customer.
- Operating System & Firewall — Customers are responsible for securing and patching the operating system they are using. The virtual private cloud (VPC) and network settings (including firewall settings) must also be carefully configured.
- Encryption — Encrypting the cloud components used is an important security mechanism, but also these settings are not applied by the public cloud provider, but by the customer.
- Network Traffic Protection — AWS, for example, provides free SSL certificates for encryption, but setting up these certificates is also up to the customer.
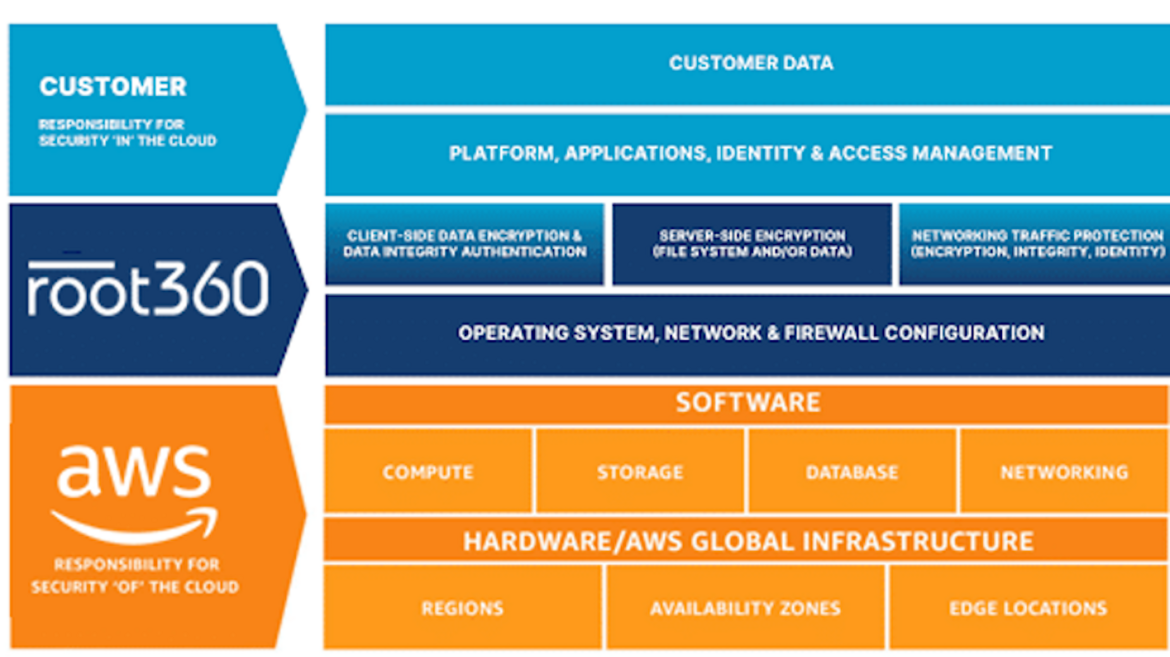
Sharing responsibility with a managed service provider
Since it is often associated with human, financial and time resources to build up know-how in your own company for using services like those from AWS, you can rely on managed service providers (MSP) such as root360. As an MSP plays a different role in the shared responsibility model, responsibilities change again in this scenario. An MSP usually takes care of the following areas:
- Operating system & firewall
- Encryption
- Network traffic protection
The customer remains responsible for:
- customer data
- application
At root360, we rely on our proven security best practices to protect the cloud environment. These include backups, AWS Shield, multi-factor authentication, AWS WAF, and more. For particularly sensitive data such as credit card information, we offer our PCI-DSS compliant AWS hosting.
Conclusion
To use the public cloud, such as the services provided by AWS, companies should collaborate with a competent partner who has the necessary experience. Building knowledge in-house involves costs and time, which can delay the move towards the cloud.
Sebastian Grau is a Sales & Partner Manager at root360 and a certified AWS Solutions Architect Associate.

Please note: The opinions expressed in Industry Insights published by dotmagazine are the author’s own and do not reflect the view of the publisher, eco – Association of the Internet Industry.


